Next: Enumeration Problem: Extreme Points
Up: Examples of Enumeration Problems
Previous: Examples of Enumeration Problems
Remarks:
- (a)
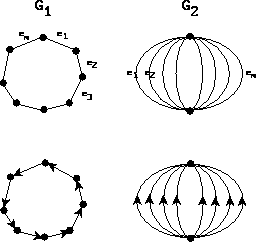
- The number of output orientations might be exponential in
the size of input, while it can be very small. Compare
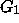 and
and 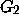 .
.
- (b)
- Is there any algorithm for the acyclic orientation problem which runs
in time polynomial in both the input size and the output size?
- (c)
- Is there such an algorithm whose space complexity is polynomial
in the size of input only (and independent of the output size)?
- (d)
- The answers to these two questions (b) and (c) are "yes."
How can you design such an algorithm? Here the reverse search technique
can be applied, see the cell enumeration in an arrangement of hyperplanes
in [AF96].
Komei Fukuda
Wed Jun 12 17:26:21 GMT+0100 1996